What is a CPU (Central Processing Unit)?
So, you want to know all about CPU’s. Join the party and get ready for the guide on CPU’s in some unnecessarily comprehensive detail. (Also, not sponsored by any retailers or websites I mention).
Contents of this article:
What’s the CPU?
Some History
Components in a computer
what’s the CPU do?
CPU specific Jargon
Cores
Threads
Clock Speeds
Overclocking
What does temperature matter?
Naming Conventions
Intel
AMD
ENOUGH! SO WHICH ONE?
What is the Central Processing Unit?
The CPU is the small inconspicuous component nested in your motherboard. It does what it says on the tin (they usually come in a box though). They are microprocessors, they process the tasks prompted by the user and they are small, hence the name; microprocessor.
(Photo of an AMD Ryzen CPU in a motherboard).
Some History
The first CPU was the Intel 4004 Microprocessor in 1971. With 2300 transistors using pMOS logic. The goal clock speed was 1MHz, it reached 740 kHz (kilohertz).1 In comparison, the clock speed of the most common CPU in 2021 is AMD’s Ryzen 7 5800X with a clock speed of 3.8 GHz (gigahertz) which is equivalent to 3 800 000 khz, roughly 5135 times faster.2 There is a perpetual Wikipedia rabbit hole on the history of computers which I would advise against going down at 3 am.
Components in a computer
The CPU is a member of the team that makes up your PC’s hardware. The CPU sits in the Motherboard which connects to the Graphics Card, SSD’s, HDD’s, M.2 drives, Cooling fans, RAM, all powered by the Power Supply.
So what’s the CPU’s job?
The CPU performs tasks like opening and running a program, exporting a video, etc. It also sends out commands to other components as it needs to work with the RAM (random access memory), graphics card, and motherboard. The components of the CPU follow the steps fetch, decode and execute to perform these tasks.3
CPU jargon you should know
First of all, if you would like to know what CPU is in your PC right now:
for windows users: hold the windows key and press R, then type msinfo32 and your system information appears. In the system summary see Processor.
Core:
The core is the CPU’s processor, they have evolved from only capable of focusing on one task at a time with one core to now multiple cores and each capable of multithreading so a CPU can perform millions of operations simultaneously, per second. In recent years, common CPU’s have between two and 18 cores, with a whopping 64 cores from AMD’s Threadripper 3990X ← coolest name ever. CPU’s can use simultaneous multithreading, synonymous with Hyper-threading (if it’s an Intel processor). so an AMD CPU would use simultaneous multithreading to provide eight threads on a four-core CPU.
Threads:
Threads are virtual, they are created when the primary thread (on the core) allocates an operation and hence, creates a thread. Threads allow the CPU to create multiple virtual cores (proportionate to the number of cores) For example a dual-core CPU has 2cores and 4 threads, and a quad-core CPU will have 4 cores, 8 threads. Each thread is created for performing a specific task. The primary thread (on the core) gets input, creates a thread, designates a task, and then does this again for the next task for 2 threads per core.4 They allow you to listen to music and simultaneously lose a friendship over cooperative rocket league. (Just kidding, sorry guys, I’ll practice).
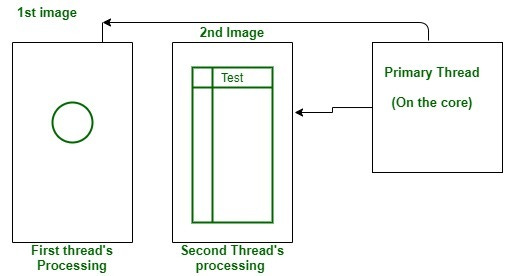
Clock Speed:
The clock speed is a measure of how long it takes for the CPU to complete a clock cycle. That is, the time for a single pulse from the CPU where it performs a basic operation, depending on the number of cores and consequently, threads, determines how many tasks it can do simultaneously. Measured in hertz and 1 hertz is the time to complete one clock cycle. Hertz is the number of cycles per second, 100 hertz is 100 cycles per second. CPU frequencies (meaning the same as clock speed) are on average 3.5GHz, 3.5 gigahertz is 3.5 billion clock cycles per second.5
If you do some maths, each thread for each task and the clock speeds accounted for, on average a CPU can carry out 100 million operations per second or more!
It is also possible to manually overclock a CPU forcing it to run faster than it’s intended to go. (you can also do this with your graphics card). Doing this increases the temperature and makes your PC a bit more volatile so it’s risky and voids any warranties. If overclocking you want a really good cooling system. There is liquid cooling or chunky fans or even liquid nitrogen for the extreme. Here’s a fun one if you want an excessive 1000 fps on doom eternal you can use liquid nitrogen to cool the processor.
Why does temperature matter?
If it gets too hot it slows down so it doesn’t catch fire. Read more in-depth about the effect CPU temperature has on performance.
“What’s in a name?
...That which we call a rose by any other name would smell just as sweet.” - Well, names do matter in this context sorry Shakey. There are two major CPU processor companies, AMD and Intel.
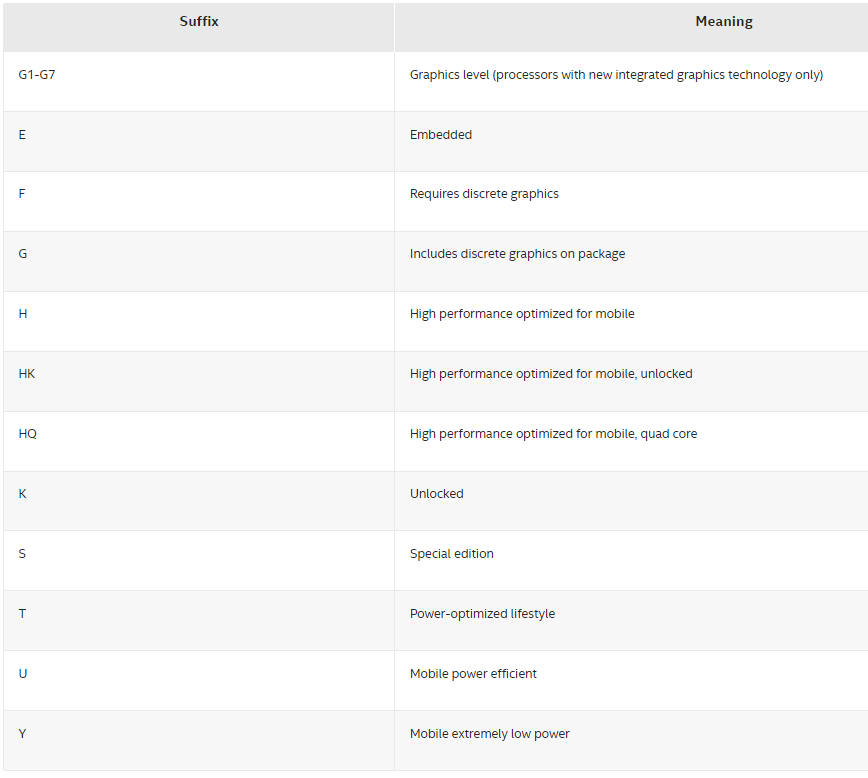
For Intel, there are the brands; Core, Xeon, Pentium, etc. The Core CPU’s are the most recent. Then comes the brand modifier. For the Core CPU’s these are; i3, i5, i7, etc. The higher the number, the better the performance. Then there is the generation number. After that the SKU which is a specific model number, a higher number within the same brand and generation usually means more features. Finally, there’s a product line suffix that indicates the capabilities. For example, a ‘U’ means it is meant for 2-in-1-laptops or XE for extreme edition.6

Here’s another nifty Intel infographic:
for AMD’s CPU’s
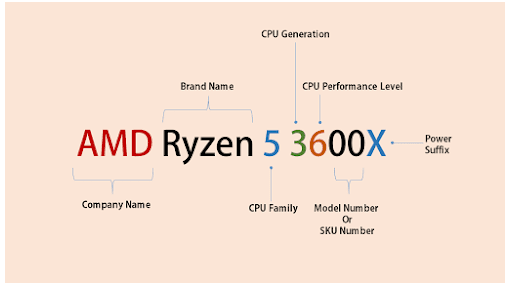
Ryzen 3’s have 4 cores and 4 threads and are budget-friendly but still have some strong options for gaming - very similar performance to intel’s i3 range. Ryzen 5’s have 4 or 6 cores etc. the higher the number the more performance the most popular brand of AMD’s are the Ryzen processors. AMD has some similarities with Intel’s naming conventions as it follows the company, brand, generation, CPU family, CPU generation, CPU performance level, model number, and power suffix. AMD has fewer suffixes than Intel.7
Enough! So which one?!!
AMD or Intel?
Depends on what you use it for and your budget. There are millions of articles on the internet recommending what you need for each specific purpose whether it be; gaming, working, both, for a $200 budget, or unlimited. But, I wrote this so that noobs like past me, and now past you, could have some more insight into the CPU market, understand what the tech reviewers are raving about, and reach your own astute and considered decision. But if you are wondering:
CPU for each budget (in $AUD):
The best CPU for Every Budget Guide. There isn’t a definitive answer for each budget as there are always price fluctuations and deals in your local area. Do your own research before buying (if you want, idk might save you some money). Or, just buy the Intel Core i9 12900K.
Here’s a great website for comparing CPU’s (and other components).
Thanks for reading, I had fun writing. If you would like to read more about tech, tech reviews, books, D&D, music, Rubik’s Cubes, coffee, and other miscellaneous interests of mine sign up for an email when I make a new post. In the next post, I’m thinking of babbling about how talent does not exist or reviewing Xenoblade Chronicles Definitive Edition.
Techspirited, 2013, History of Computer Processors
WhatPSU, 2021, CPU Popularity 2021
David Both, 2021, The central processing unit (CPU): Its components and functionality
rajkumaruttam90, 2020, What are Threads in Computer Processor or CPU?
Josh Fewell, 2020, Processor Speed - Cores, Threads, and Clock Speed
Intel Corporation, 2020, Intel Processor Names and Numbers
Lets Letch Ready, 2020, AMD Ryzen Processors naming scheme




